Economy
Philippine Peso Expected to Stabilize Around 58 Despite Recent Volatility
Juancho Mabini
24 Jan, 2026
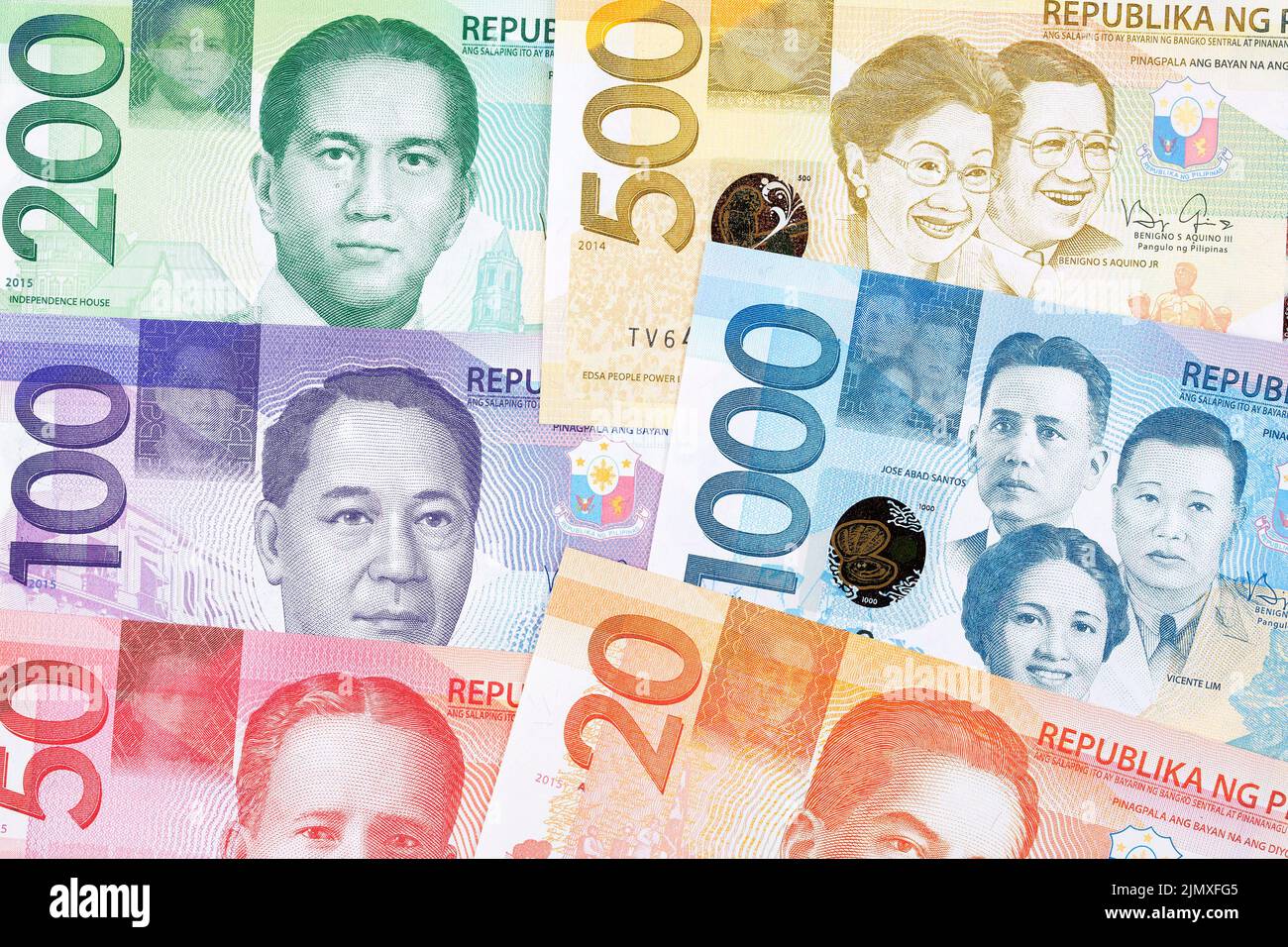

MANILA – The Philippine peso is anticipated to remain stable around the 58 level against the US dollar this year and into 2026, even after recent fluctuations approaching the 59 mark.
Corrie Purisima, Treasurer and Head of Markets and Security at HSBC, shared insights during the Makati Business Club’s year-end review and 2026 outlook event, "Beyond the Numbers," in Makati City. Drawing from their economist’s forecast, she highlighted that further depreciation to 60 is unlikely.
"We expect the peso to hover around the 58 level in the near term. This is primarily due to anticipated declines in import volume as infrastructure spending slows, reducing downward pressure on the currency," Purisima explained.
She added that slower imports will be balanced by consistent inflows from the business process outsourcing (BPO) sector and remittances sent by overseas Filipino workers, which collectively reach approximately USD 35 to 36 billion annually. "These stable inflows continue to support currency stability," she noted.
However, Purisima acknowledged ongoing currency pressures linked to the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas’s dovish monetary policy stance, which includes possible rate cuts of 25 basis points next month and another in the following year. Furthermore, she cited risks of a stronger US dollar, influenced by decreasing odds of Federal Reserve rate reductions amid persistent inflation concerns.
"These factors should balance out, maintaining the peso near the 58 mark for the year," she added.
Karl Chua, Managing Director of Ayala Corporation, also weighed in during the event, endorsing the Bangko Sentral’s approach of allowing market forces to determine the peso’s trajectory. "Maintaining a free-floating exchange rate based on supply and demand is a prudent policy," he stated.
Chua acknowledged that certain sectors, including exporters and importers, may face challenges but emphasized the importance of focusing on the real exchange rate adjusted for inflation and productivity rather than the nominal rate.
Meanwhile, Nicholas Mapa, chief economist and market strategist at Metropolitan Bank & Trust Company (Metrobank), projected a generally weak US dollar through 2026, influenced by the Federal Reserve’s anticipated rate-cutting cycle. Nonetheless, he cautioned that Philippine-specific dynamics, such as projected current account deficits in 2026 and 2027, could sustain pressure on the peso.
"While the peso may experience some depreciation, external and domestic factors will ultimately shape its trajectory," Mapa concluded.
Recommended For You

DSWD Urges Public to Support Indigenous Peoples and Street Families Through Organized Programs, Not Alms
Jan 24, 2026
Juancho Mabini
DigiPlus Interactive Plans Localized Livestream Bingo for Brazil Market
Jan 24, 2026
Dorotea Balagtas
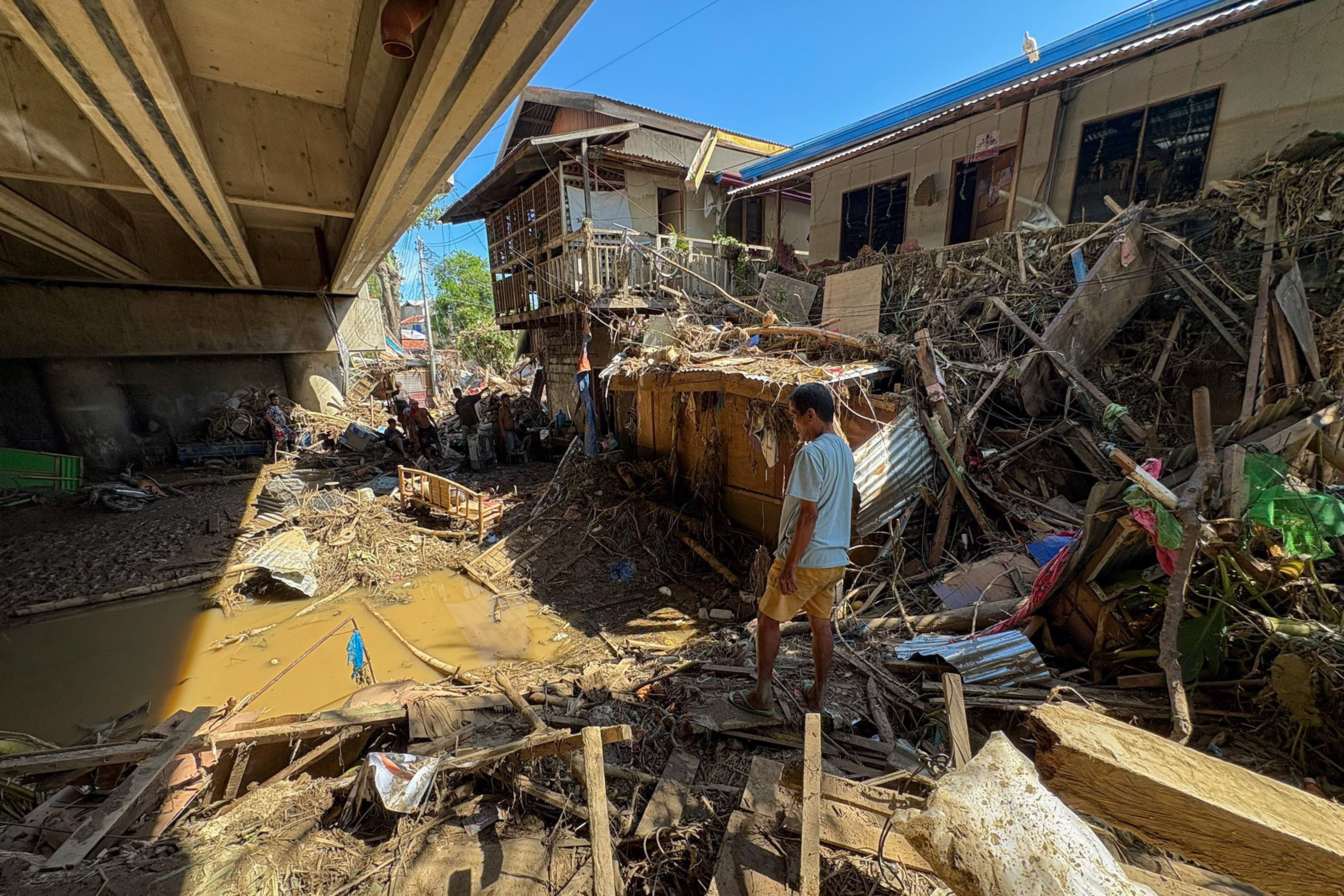

Super Typhoon Uwan Causes Over PHP4 Billion in Agricultural and Infrastructure Losses
Jan 24, 2026
Isagani Llorente

Oriental Mindoro Governor Commends Teams for Successful 75th Founding Anniversary Celebration
Jan 24, 2026
Ligaya Almeda
